Edge Computing-Based Visual Guidance System
Abstract
This post describes the development of a visual guidance system for a flying vehicle, leveraging edge computing for real-time target detection and attitude control.
i. System Design
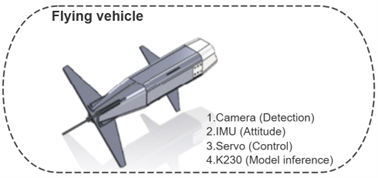
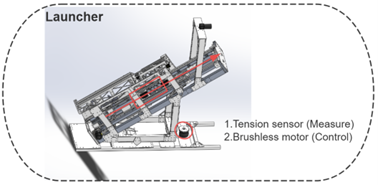
Designed a system comprising a launcher and a flying vehicle. The flying vehicle is capable of recognizing and precisely striking ground targets. It relies on initial velocity for flight, adjusts its attitude via a tail wing, and achieves target accuracy through visual guidance. The launcher provides initial velocity, controls thrust using a tension sensor, and adjusts the vehicle’s yaw angle during launch with a motor.
ii. Control Methodology
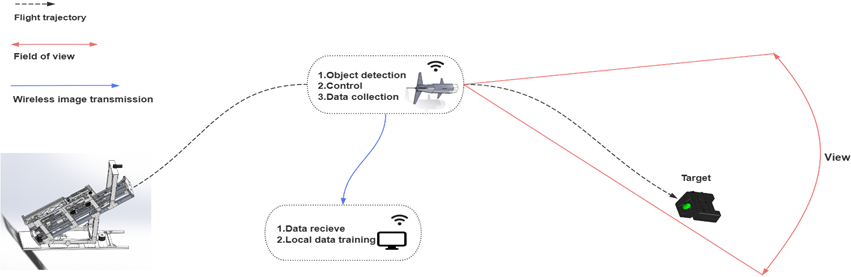
Leveraged edge computing for real-time target detection and vehicle attitude control. The visual guidance system integrates precise target recognition with adaptive attitude adjustment to ensure high-accuracy strikes.
iii. Hardware Implementation
- Integrated an embedded NPU (K230) for real-time inference of the target detection model. Used an embedded CPU (K230) to control servo motors that adjust the vehicle’s tail wing for attitude regulation.
- Incorporated an IMU to acquire real-time attitude data of the flying vehicle.
- Implemented an embedded Free-RTOS system to manage the launcher’s thrust control and yaw angle adjustment during operation.
iv. Software Development
Developed and trained the target detection model, optimized it for deployment on the embedded NPU, and implemented robust control algorithms for vehicle attitude and launcher operations.
v. Experimental Validation
Conducted comprehensive tests to validate the system’s performance under various conditions, ensuring its ability to recognize targets, adjust flight dynamics, and achieve precise strikes.
Pictures
- i.
- ii.
- iii.
For more information about this theme, you can search the repository.